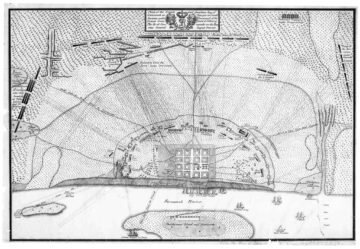
The Siege of Savannah
September 16 – October 18, 1779 at Savannah, Georgia

Battle Summary
The Siege of Savannah was also known as the Second Battle of Savannah.. The year before, the city of Savannah, Georgia, had been captured by a British expeditionary corps under Lieutenant Colonel Archibald Campbell. The siege itself consisted of a joint Franco-American attempt to retake Savannah, from September 16 to October 18, 1779.
On October 9, a major assault against the British siege works failed. During the attack, Polish nobleman Brigadier General Casimir Pułaski, leading the combined cavalry forces on the American side, was mortally wounded. With the failure of the joint attack, the siege was abandoned, and the British remained in control of Savannah until July 1782, near the end of the war.
In 1779, more than 500 recruits from Saint-Domingue (the French colony which later became Haiti), under the overall command of French nobleman Charles Hector, Comte d'Estaing, fought alongside American colonial troops against the British Army during the siege of Savannah.
This was one of the most significant, foreign contributions to the Revolutionary War. This French-colonial force had been established six months earlier and included hundreds of soldiers of color in addition to white soldiers and a couple black slaves.
Facts about the Siege of Savannah
- Armies - American Forces was commanded by Maj. Gen. Benjamin Lincoln and consisted of between 5,050 Soldiers. British Forces was commanded by Gen. Augustine Prevost and consisted of between 3,200 Soldiers.
- Casualties - American casualties were estimated to be 244 killed, 584 wounded, and 120 captured. British casualties were estimated to be 40 killed, 63 wounded, and 52 missing.
- Outcome - The result of the Siege was a British victory. The Siege was part of the Southern Theater 1775-82.
Prelude
Following the failures of military campaigns in the northern United States earlier in the Revolutionary War, British military planners decided to embark on a southern strategy to conquer the rebellious colonies, with the support of Loyalists in the South. Their first step was to gain control of the southern ports of Savannah, Georgia and Charleston, South Carolina. An expedition in December 1778 took Savannah with modest resistance from ineffective militia and Continental Army defenses.
The Continental Army regrouped, and by June 1779, the combined army and militia forces guarding Charleston numbered between 5,000 and 7,000 men. Major General Benjamin Lincoln, commanding those forces, knew that he could not recapture Savannah without naval assistance; for this he turned to the French, who had entered the war as an American ally in 1778.
French Admiral the Comte d'Estaing spent the first part of 1779 in the Caribbean, where his fleet and a British fleet monitored each other's movements. He took advantage of conditions to capture Grenada in July before acceding to American requests for support in operations against Savannah.

American and French troops attacking Spring Hill Redoubt at the Battle of Savannah on 9th October 1779
On September 3, an uncharacteristically early arrival as there was still substantial risk of seasonal hurricanes—a few French ships arrived at Charleston with news that d'Estaing was sailing for Georgia with 25 ships of the line and 4,000 French troops. Lincoln and the French emissaries agreed on a plan of attack on Savannah, and Lincoln left Charleston with over 2,000 men on September 11.
British troop strength in the area consisted of about 6,500 regulars at Brunswick, Georgia, another 900 at Beaufort, South Carolina, under Colonel John Maitland, and about 100 Loyalists at Sunbury, Georgia. Major General Augustine Prevost, in command of these troops from his base at Savannah, was caught unprepared when the French fleet began to arrive off Tybee Island near Savannah and recalled the troops stationed at Beaufort and Sunbury to aid in the city's defense.
Captain Moncrief of the Royal Engineers was tasked with constructing fortifications to repulse the invaders. Using 500–800 slaves working up to twelve hours per day, Moncrief constructed an entrenched defensive line, which included redoubts, nearly 1,200 feet long, on the plains outside the city.
The British Royal Navy contributed two over-age frigates, HMS Fowey and HMS Rose. They landed their guns and most of their men to reinforce the land forces. In addition, the British also deployed the armed brig Keppel and the armed ship Germaine, the latter from the East Florida navy. There were two galleys, Comet and Thunder, also from East Florida. Lastly, the British armed two merchant vessels, Savannah and Venus.
Battle Begins
On September 12, D'Estaing began landing troops below the city and began moving in by September 16. Confident of victory, and believing that Maitland's reinforcements would be prevented from reaching Savannah by Lincoln, he offered Prevost the opportunity to surrender. Prevost delayed, asking for 24 hours of truce.
Owing to miscommunication about who was responsible for preventing Maitland's movements, the waterways separating South Carolina's Hilton Head Island from the mainland were left unguarded, and Maitland was able to reach Savannah hours before the truce ended. Prevost's response to d'Estaing's offer was a polite refusal, despite the arrival of Lincoln's forces.
On September 19, as Charles-Marie de Trolong du Rumain moved his squadron up the river, he exchanged fire with Comet, Thunder, Savannah, and Venus. The next day, the British scuttled Rose, which was leaking badly, just below the town to impede the French vessels from progressing further. They also burnt Savannah and Venus. By scuttling Rose in a narrow part of the channel, the British effectively blocked it. Consequently, the French fleet was unable to assist the American assault.
Germaine took up a position to protect the north side of Savannah's defenses. Comet and Thunder had the mission of opposing any attempt by the South Carolinian galleys to bombard the town. Over the next few days, British shore batteries assisted Comet and Thunder in engagements with the two South Carolinian galleys; during one of these, they severely damaged Revenge.
The French commander, rejecting the idea of assaulting the British defenses, unloaded cannons from his ships and began a bombardment of the city. The city, rather than the entrenched defenses, bore the brunt of this bombardment, which lasted from October 3 to 8. "The appearance of the town afforded a melancholy prospect, for there was hardly a house that had not been shot through", wrote one British observer.
When the bombardment failed to have the desired effect, d'Estaing changed his mind, and decided it was time to try an assault. He was motivated in part by the desire to finish the operation quickly, as scurvy and dysentery were becoming problems on his ships, and some of his supplies were running low. While a traditional siege operation would likely have succeeded eventually, it would have taken longer than d'Estaing was prepared to stay.

Sergeant Jasper on the parapet of the Spring Hill Redoubt during the attack on Savannah on 9th October 1779
On October 9, against the advice of many of his officers, d'Estaing launched the assault against the British position that morning. The success depended in part on the secrecy of some its aspects, which were betrayed to Prevost well before the operations were supposed to begin around 4:00 AM.
Fog caused troops attacking the Spring Hill redoubt to get lost in the swamps, and it was nearly daylight when the attack finally got underway. The redoubt on the right side of the British works had been chosen by the French admiral in part because he believed it to be defended only by militia.
In fact, it was defended by a combination of militia and Scotsmen from John Maitland's 71st Regiment of Foot, Fraser's Highlanders, who had distinguished themselves at Stono Ferry. The militia included riflemen, who easily picked-off the white-clad French troops when the assault was underway.
Admiral d'Estaing was twice wounded and Pułaski was mortally wounded. By the time the second wave arrived near the redoubt, the first wave was in complete disarray, and the trenches below the redoubt were filled with bodies. Attacks intended as feints against other redoubts of the British position were easily taken.
The second assault column was commanded by the Swedish Count Curt von Stedingk, who managed to reach the last trench. He later wrote in his journal, "I had the pleasure of planting the American flag on the last trench, but the enemy renewed its attack and our people were annihilated by cross-fire". He was forced back by overwhelming numbers of British troops, left with some 20 men—all were wounded, including von Stedingk. He later wrote, "The moment of retreat with the cries of our dying comrades piercing my heart was the bitterest of my life". After an hour of carnage, d'Estaing ordered a retreat.
On October 17, Lincoln and d'Estaing abandoned the siege.
Aftermath

Attack of 2nd South Carolina Continentals on the Spring Hill Redoubt at the Siege of Savannah on 9th October 1779
The battle was one of the bloodiest of the war. General Henry Clinton wrote, "I think that this is the greatest event that has happened the whole war," and celebratory cannons were fired when the news reached London.
After this battle, d'Estaing returned to France and Pulaski was taken to the USS Wasp and was buried at sea on October 15.
Both the American and the French remained in the area until October 16, when Lincoln began an orderly withdrawal to Charleston.